Product Description
ETERNOO MACHINERY CO., LTD is 1 professional and excellent Corporation engaged in designing and producing machinery and materials for the field of Prestressed Concrete Industry and Post Tensioning Industry in construction and argriculture field in China, which is a manufacture and an international trading enterprise.
The company established in year 2008, under the guidance of reform and opening-up policy and with the help of government at all levels, with all of our staffs hardworking, has continuously developed at steady speed. At present, Our company has a total staff of 60, a workshop area of 2400m2, mechanical equipment manufacturing base at HangZhou. The company,with stable strength advantages in the brand, quality, technology, market, scale and benefit, has been making contribution to the local economic development.
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Machinery, Marine, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Double Helical Gear |
| Material: | Cast Steel |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
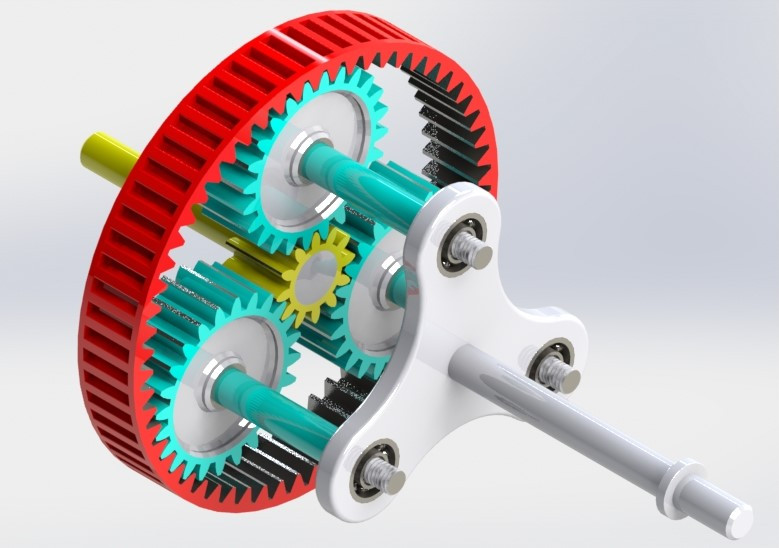
How do planetary gears handle changes in speed and torque distribution?
Planetary gears are capable of effectively handling changes in speed and torque distribution due to their unique design and configuration. Let’s explore how planetary gears handle these changes:
- Speed Changes:
Planetary gears can handle speed changes by utilizing the different gear ratios they offer. By adjusting the sizes and numbers of teeth on the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, different gear ratios can be achieved. When the input speed is applied to the sun gear, it gets transmitted to the planet gears, resulting in a specific output speed. By changing the gear ratio, the output speed can be adjusted accordingly. This ability to vary the gear ratio allows planetary gears to adapt to different speed requirements in mechanical systems.
- Torque Distribution:
Planetary gears excel in distributing torque across multiple gear teeth, ensuring efficient torque transmission and load sharing. The planet gears are meshed with both the sun gear and the ring gear, enabling torque to be transmitted through multiple contact points simultaneously. This distributed torque distribution helps in reducing stress on individual gear teeth and enhances the overall torque-carrying capacity of the gear system. The load is shared among the planet gears, preventing excessive wear and minimizing the risk of gear failure.
- Torque Amplification:
Planetary gears can also handle torque amplification, allowing for increased torque output compared to the input torque. By fixing the ring gear and inputting power to the sun gear, the planet gears rotate and contribute to multiplying the torque. The arrangement of multiple gear sets in a compact design enables torque amplification, making planetary gears suitable for applications that require high torque output while maintaining a smaller physical size.
- Load Balancing:
Another aspect of torque distribution in planetary gears is load balancing. The planet gears distribute the load across multiple gear teeth, reducing the concentration of forces on individual teeth. This load balancing capability results in improved gear system durability and longevity. It also helps in minimizing vibration, noise, and wear, ensuring smoother and more reliable operation.
- Flexible Configuration:
Planetary gears offer flexibility in their configuration, allowing for the accommodation of changes in speed and torque distribution. The number of planet gears, the size of the gears, and their arrangement can be adjusted to meet specific application requirements. This flexibility enables planetary gears to handle a wide range of speed and torque variations, making them adaptable to different mechanical setups.
In summary, planetary gears handle changes in speed and torque distribution through their ability to adjust gear ratios, distribute torque across multiple gear teeth, amplify torque, balance loads, and accommodate flexible configurations. These characteristics make planetary gears suitable for applications that require precise control over speed and torque, efficient power transmission, and reliable performance.
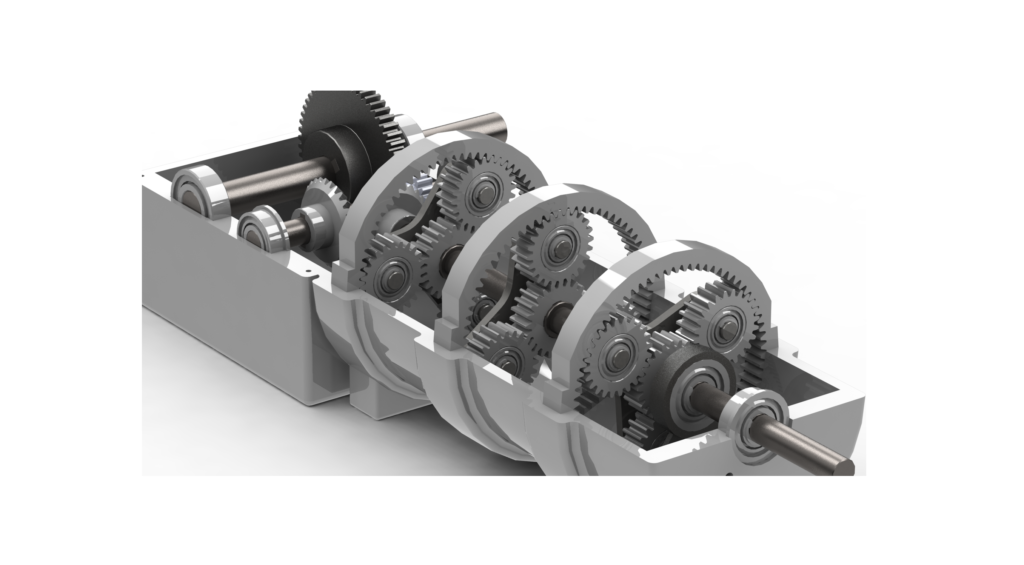
Can you explain the process of gear shifting in planetary gear systems?
Gear shifting in planetary gear systems involves changing the gear ratio by engaging or disengaging specific components of the gear set. Let’s explore the process of gear shifting in more detail:
- Clutching and Braking:
The gear shifting process in planetary gear systems primarily relies on clutching and braking mechanisms. These mechanisms selectively connect or disconnect various gears within the system to achieve the desired gear ratio. Here are the key steps involved:
- Clutch Engagement:
To shift to a higher gear ratio, the clutch associated with the gear component that needs to be engaged is activated. The clutch connects the rotating member, such as the sun gear, planet carrier, or ring gear, to the stationary member, allowing torque transmission. This engagement results in a change in the gear ratio, leading to higher speed or torque output depending on the specific gear set configuration.
- Brake Application:
On the other hand, to shift to a lower gear ratio, a brake associated with the gear component that needs to be disengaged is applied. The brake immobilizes or slows down the rotation of the selected gear element, preventing it from transmitting torque. By selectively braking certain components, the gear ratio is altered, resulting in a lower speed or higher torque output.
- Sequential Shifting:
In some planetary gear systems, gear shifting is performed sequentially. This means that one gear component is engaged or disengaged at a time, gradually transitioning from one gear ratio to another. Sequential shifting allows for smooth and controlled gear changes, minimizing the stress on the transmission components and ensuring seamless power transmission.
- Electronic Control:
In modern applications, gear shifting in planetary gear systems is often electronically controlled. Electronic control systems utilize sensors, actuators, and a control unit to monitor various parameters such as vehicle speed, engine load, and driver input. Based on these inputs, the control unit determines the optimal gear shift points and actuates the clutches and brakes accordingly. Electronic control enhances the efficiency, precision, and automation of the gear shifting process.
In summary, gear shifting in planetary gear systems involves the engagement and disengagement of clutches and brakes to alter the gear ratio. By selectively connecting or disconnecting specific gear components, the speed and torque output can be adjusted. Sequential shifting and electronic control systems further enhance the gear shifting process, providing smooth and efficient operation in various applications, including automotive transmissions and industrial machinery.

What is the purpose of using planetary gears in machinery?
Planetary gears serve several important purposes in machinery and mechanical systems. Let’s delve into the key purposes and benefits of using planetary gears:
- Gear Ratio Variation:
One of the primary purposes of planetary gears is to achieve different gear ratios. By varying the number of teeth on the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, a wide range of gear ratios can be obtained. This flexibility enables machinery to adapt to varying speed and torque requirements, allowing for precise control and efficient power transmission.
- Torque Amplification:
Planetary gears are known for their ability to amplify torque. The arrangement of multiple gear sets in a compact design allows for torque multiplication. This can be particularly beneficial in applications where high torque is required while maintaining a smaller form factor. Planetary gears can efficiently transmit torque and handle heavy loads.
- Compact Size:
Another advantage of planetary gears is their compact size. The internal gear meshing and the integration of multiple gear sets within a single gear system contribute to their space-saving design. This compactness is valuable in machinery where space constraints are a consideration, enabling the design of more compact and lightweight systems.
- High Efficiency:
Planetary gears are known for their high efficiency in power transmission. The internal gear meshing and the distribution of load across multiple gear teeth result in efficient torque transfer with minimal power loss. This efficiency is crucial in machinery where energy conservation and optimization are important factors.
- Directional Control:
Planetary gears allow for bidirectional power transmission. By controlling the direction of rotation of the input and output elements, the direction of rotation in the machinery can be easily changed. This feature is useful in applications that require reversing the direction of rotation or changing the rotational direction without the need for additional mechanisms.
- Shock Absorption:
The arrangement of multiple gears in a planetary gear system provides inherent shock-absorbing capabilities. The distributed load between the gear teeth helps to dampen vibrations and absorb shocks, contributing to smoother operation and reduced wear on the system components.
- Application Versatility:
Planetary gears find applications in a wide range of machinery and mechanical systems. They are commonly used in automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, robotics, aerospace systems, power generation equipment, and more. The versatility of planetary gears stems from their ability to provide precise control, compactness, high torque transmission, and efficient power transmission.
In summary, the purpose of using planetary gears in machinery is to achieve variable gear ratios, amplify torque, maintain compact size, ensure high efficiency in power transmission, enable bidirectional control, absorb shocks, and provide versatility for various applications. The unique characteristics of planetary gears make them valuable components in diverse machinery and mechanical systems.


editor by CX 2023-11-02