Product Description
TaiBang Motor Industry Group Co., Ltd.
The main products is induction motor, reversible motor, DC brush gear motor, DC brushless gear motor, CH/CV big gear motors, Planetary gear motor ,Worm gear motor etc, which used widely in various fields of manufacturing pipelining, transportation, food, medicine, printing, fabric, packing, office, apparatus, entertainment etc, and is the preferred and matched product for automatic machine.
Model Instruction
GB090-10-P2
| GB | 090 | 571 | P2 |
| Reducer Series Code | External Diameter | Reduction Ratio | Reducer Backlash |
| GB:High Precision Square Flange Output
GBR:High Precision Right Angle Square Flange Output GE:High Precision Round Flange Output GER:High Precision Right Round Flange Output |
050:ø50mm 070:ø70mm 090:ø90mm 120:ø120mm 155:ø155mm 205:ø205mm 235:ø235mm 042:42x42mm 060:60x60mm 090:90x90mm 115:115x115mm 142:142x142mm 180:180x180mm 220:220x220mm |
571 means 1:10 | P0:High Precision Backlash
P1:Precison Backlash P2:Standard Backlash |
Main Technical Performance
| Item | Number of stage | Reduction Ratio | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB090 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 |
| Rotary Inertia | 1 | 3 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.61 | 3.25 | 9.21 | 28.98 | 69.61 | ||
| 4 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 2.74 | 7.54 | 23.67 | 54.37 | ||||
| 5 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | 53.27 | ||||
| 6 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.65 | 7.25 | 22.75 | 51.72 | ||||
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.45 | 2.62 | 7.14 | 22.48 | 50.97 | ||||
| 8 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.58 | 7.07 | 22.59 | 50.84 | ||||
| 9 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.04 | 22.53 | 50.63 | ||||
| 10 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | 50.56 | ||||
| 2 | 15 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | |
| 20 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 25 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 35 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 40 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 45 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 2.71 | 7.42 | 23.29 | ||
| 50 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 60 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 70 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 80 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 | ||
| 100 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 2.57 | 7.03 | 22.51 |
| Item | Number of stage | GB042 | GB060 | GB060A | GB90 | GB090A | GB115 | GB142 | GB180 | GB220 | |
| Backlash(arcmin) | High Precision P0 | 1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||
| 2 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |||||||
| Precision P1 | 1 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | ≤3 | |
| 2 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ||
| Standard P2 | 1 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | ≤5 | |
| 2 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ≤7 | ||
| Torsional Rigidity(N.M/arcmin) | 1 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | |
| 2 | 3 | 7 | 7 | 14 | 14 | 25 | 50 | 145 | 225 | ||
| Noise(dB) | 1,2 | ≤56 | ≤58 | ≤58 | ≤60 | ≤60 | ≤63 | ≤65 | ≤67 | ≤70 | |
| Rated input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 5000 | 5000 | 5000 | 4000 | 4000 | 4000 | 3000 | 3000 | 2000 | |
| Max input speed(rpm) | 1,2 | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 8000 | 8000 | 8000 | 6000 | 6000 | 4000 | |
Noise test standard:Distance 1m,no load.Measured with an input speed 3000rpm
| Application: | Machinery, Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Change Drive Direction, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Cycloidal |
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Installation: | Vertical Type |
| Step: | Double-Step |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
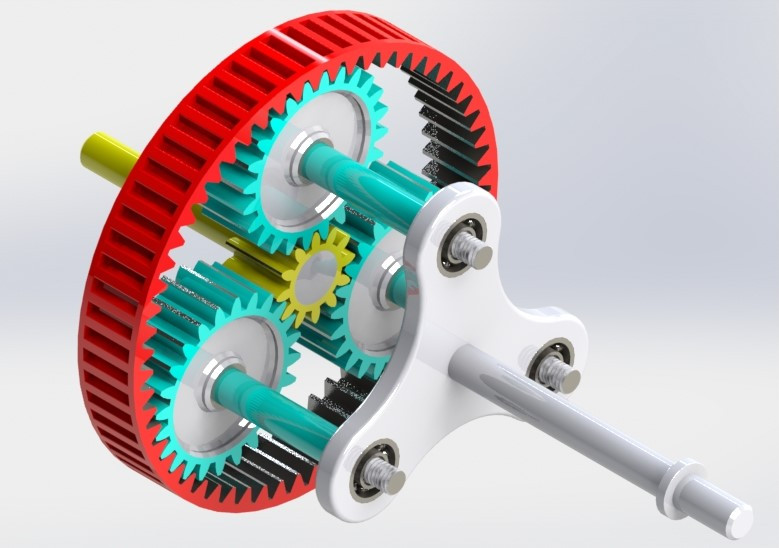
How do planetary gears handle changes in speed and torque distribution?
Planetary gears are capable of effectively handling changes in speed and torque distribution due to their unique design and configuration. Let’s explore how planetary gears handle these changes:
- Speed Changes:
Planetary gears can handle speed changes by utilizing the different gear ratios they offer. By adjusting the sizes and numbers of teeth on the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear, different gear ratios can be achieved. When the input speed is applied to the sun gear, it gets transmitted to the planet gears, resulting in a specific output speed. By changing the gear ratio, the output speed can be adjusted accordingly. This ability to vary the gear ratio allows planetary gears to adapt to different speed requirements in mechanical systems.
- Torque Distribution:
Planetary gears excel in distributing torque across multiple gear teeth, ensuring efficient torque transmission and load sharing. The planet gears are meshed with both the sun gear and the ring gear, enabling torque to be transmitted through multiple contact points simultaneously. This distributed torque distribution helps in reducing stress on individual gear teeth and enhances the overall torque-carrying capacity of the gear system. The load is shared among the planet gears, preventing excessive wear and minimizing the risk of gear failure.
- Torque Amplification:
Planetary gears can also handle torque amplification, allowing for increased torque output compared to the input torque. By fixing the ring gear and inputting power to the sun gear, the planet gears rotate and contribute to multiplying the torque. The arrangement of multiple gear sets in a compact design enables torque amplification, making planetary gears suitable for applications that require high torque output while maintaining a smaller physical size.
- Load Balancing:
Another aspect of torque distribution in planetary gears is load balancing. The planet gears distribute the load across multiple gear teeth, reducing the concentration of forces on individual teeth. This load balancing capability results in improved gear system durability and longevity. It also helps in minimizing vibration, noise, and wear, ensuring smoother and more reliable operation.
- Flexible Configuration:
Planetary gears offer flexibility in their configuration, allowing for the accommodation of changes in speed and torque distribution. The number of planet gears, the size of the gears, and their arrangement can be adjusted to meet specific application requirements. This flexibility enables planetary gears to handle a wide range of speed and torque variations, making them adaptable to different mechanical setups.
In summary, planetary gears handle changes in speed and torque distribution through their ability to adjust gear ratios, distribute torque across multiple gear teeth, amplify torque, balance loads, and accommodate flexible configurations. These characteristics make planetary gears suitable for applications that require precise control over speed and torque, efficient power transmission, and reliable performance.
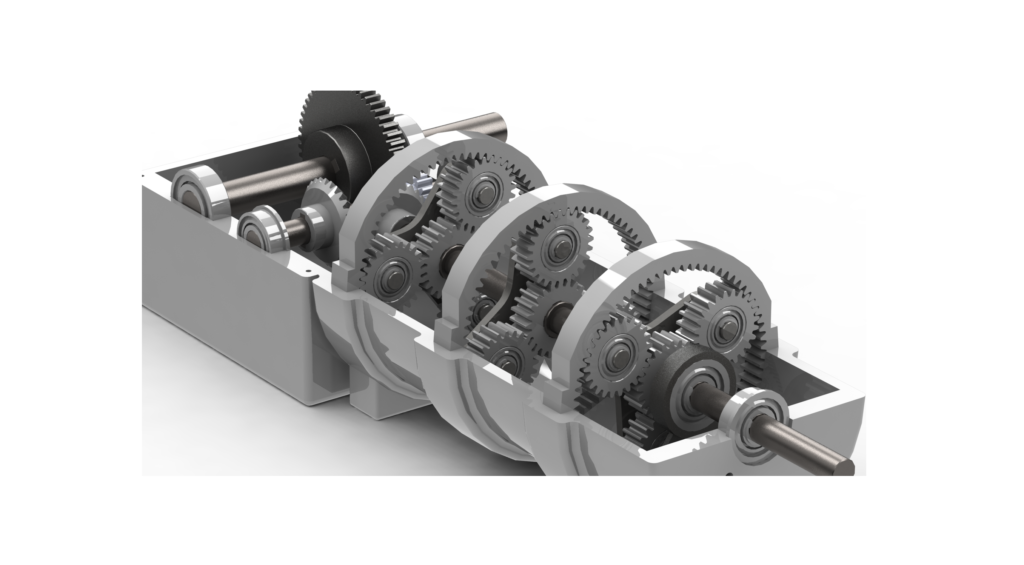
Can you explain the process of gear shifting in planetary gear systems?
Gear shifting in planetary gear systems involves changing the gear ratio by engaging or disengaging specific components of the gear set. Let’s explore the process of gear shifting in more detail:
- Clutching and Braking:
The gear shifting process in planetary gear systems primarily relies on clutching and braking mechanisms. These mechanisms selectively connect or disconnect various gears within the system to achieve the desired gear ratio. Here are the key steps involved:
- Clutch Engagement:
To shift to a higher gear ratio, the clutch associated with the gear component that needs to be engaged is activated. The clutch connects the rotating member, such as the sun gear, planet carrier, or ring gear, to the stationary member, allowing torque transmission. This engagement results in a change in the gear ratio, leading to higher speed or torque output depending on the specific gear set configuration.
- Brake Application:
On the other hand, to shift to a lower gear ratio, a brake associated with the gear component that needs to be disengaged is applied. The brake immobilizes or slows down the rotation of the selected gear element, preventing it from transmitting torque. By selectively braking certain components, the gear ratio is altered, resulting in a lower speed or higher torque output.
- Sequential Shifting:
In some planetary gear systems, gear shifting is performed sequentially. This means that one gear component is engaged or disengaged at a time, gradually transitioning from one gear ratio to another. Sequential shifting allows for smooth and controlled gear changes, minimizing the stress on the transmission components and ensuring seamless power transmission.
- Electronic Control:
In modern applications, gear shifting in planetary gear systems is often electronically controlled. Electronic control systems utilize sensors, actuators, and a control unit to monitor various parameters such as vehicle speed, engine load, and driver input. Based on these inputs, the control unit determines the optimal gear shift points and actuates the clutches and brakes accordingly. Electronic control enhances the efficiency, precision, and automation of the gear shifting process.
In summary, gear shifting in planetary gear systems involves the engagement and disengagement of clutches and brakes to alter the gear ratio. By selectively connecting or disconnecting specific gear components, the speed and torque output can be adjusted. Sequential shifting and electronic control systems further enhance the gear shifting process, providing smooth and efficient operation in various applications, including automotive transmissions and industrial machinery.
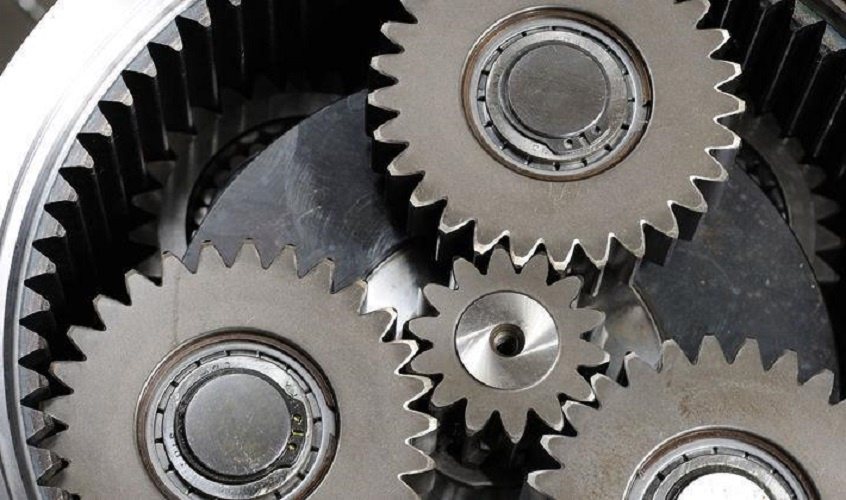

Can you describe the role of sun gears, planet gears, and ring gears in planetary systems?
In a planetary gear system, each component—the sun gear, planet gears, and ring gear—plays a crucial role in the overall operation and functionality. Let’s explore the roles of these gears:
- Sun Gear:
The sun gear is a central component in a planetary gear system. It is typically located at the center and is driven by an input source such as a motor or engine. The sun gear receives the input power and transmits it to the other gears in the system. As the sun gear rotates, it drives the rotation of the planet gears, which, in turn, contribute to the overall gear operation. The size and number of teeth on the sun gear determine the gear ratio and torque characteristics of the system.
- Planet Gears:
The planet gears are gears that surround the sun gear in a planetary gear system. They are typically smaller in size compared to the sun gear and are connected to a carrier or arm. The planet gears mesh with both the sun gear and the ring gear. As the sun gear rotates, it drives the rotation of the planet gears. The planet gears exhibit both rotational and orbital motion. While they rotate on their own axes, they also orbit around the sun gear. This combination of rotational and orbital movement allows the planet gears to transmit torque and contribute to the overall gear reduction or amplification. The arrangement and number of planet gears can vary depending on the specific design and requirements of the system.
- Ring Gear:
The ring gear is the outermost gear in a planetary gear system. It has internal teeth that mesh with the planet gears. The ring gear remains fixed or stationary while the sun gear and planet gears rotate. The interaction between the planet gears and the ring gear enables the gear system to achieve gear reduction or amplification. The size and number of teeth on the ring gear also influence the gear ratio and torque characteristics of the system.
In summary, the sun gear serves as the primary driver, receiving the input power and transmitting it to the other gears. The planet gears rotate and orbit around the sun gear, contributing to torque transmission and gear functionality. The ring gear remains fixed and meshes with the planet gears, allowing for gear reduction or amplification. Together, these gears work in harmony to achieve the desired gear ratios, torque transmission, and overall operation of planetary gear systems.


editor by CX 2023-11-29